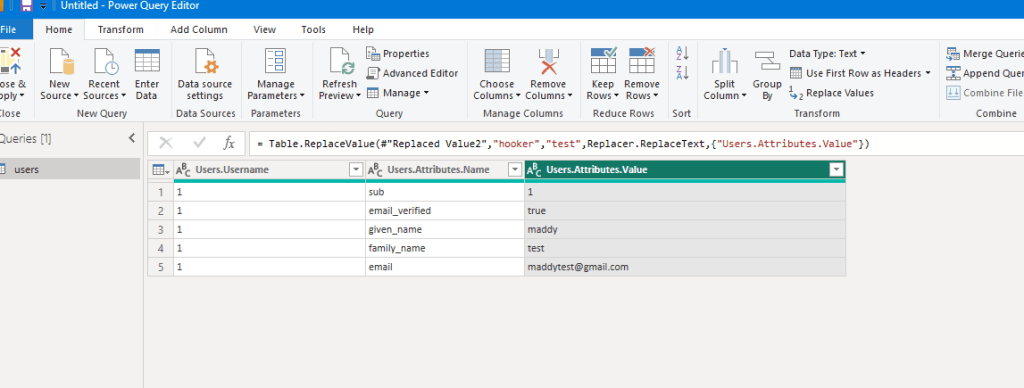
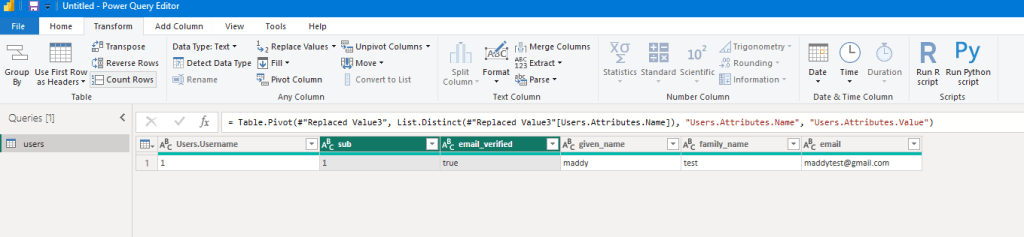
Creating a Jenkins pipeline involves defining a script that specifies the entire build process, including stages, steps, and conditions. Jenkins Pipeline can be created using either Declarative or Scripted syntax. Below, I’ll provide a simple example using both syntaxes.
Declarative Pipeline:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo 'Building the project'
// Your build steps go here
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
echo 'Running tests'
// Your test steps go here
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
echo 'Deploying the application'
// Your deployment steps go here
}
}
}
}
In this example:
agent anyspecifies that the pipeline can run on any available agent.stagesdefine the different phases of the pipeline.- Inside each
stage, you havestepswhere you define the tasks to be executed.
Scripted Pipeline:
Scripted pipelines use a more programmatic approach with a Groovy-based DSL. Here’s an example:
node {
// Define the build stage
stage('Build') {
echo 'Building the project'
// Your build steps go here
}
// Define the test stage
stage('Test') {
echo 'Running tests'
// Your test steps go here
}
// Define the deploy stage
stage('Deploy') {
echo 'Deploying the application'
// Your deployment steps go here
}
}
In this example:
nodespecifies that the entire pipeline will run on a single agent.- Inside each
stage, you have the code for the corresponding tasks.
Pipeline Setup in Jenkins
- Install the Docker Pipeline Plugin:
- Navigate to “Manage Jenkins” > “Manage Plugins” in the Jenkins Classic UI.
- Switch to the “Available” tab, search for “Docker Pipeline,” and check the box next to it.
- Click “Install without restart.”
- Restart Jenkins:
- After installing the Docker Pipeline Plugin, restart Jenkins to ensure the plugin is ready for use.
- Create a Jenkinsfile in Your Repository:
- Copy the above script (declarative or scripted) to a file named ‘Jenkinsfile’.
- Create a New Multibranch Pipeline in Jenkins:
- In the Jenkins Classic UI, click on “New Item” in the left column.
- Provide a name for your new item (e.g., My-Pipeline).
- Select “Multibranch Pipeline” as the project type.
- Click “OK.”
- Configure Repository Source:
- Click the “Add Source” button.
- Choose the type of repository you want to use (e.g., Git, GitHub, Bitbucket) and fill in the required details (repository URL, credentials, etc.).
- Save and Run Your Pipeline:
- Click the “Save” button.
- Jenkins will automatically detect branches in your repository and start running the pipeline.
This is a very basic example. Depending on your project, you may need to add more advanced features, such as parallel execution, input prompts, error handling, and integration with external tools.
Make sure to refer to the official Jenkins Pipeline documentation for more in-depth information and advanced features.